K Means Clustering Algorithm implemented. More...
#include <float.h>#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>Data Structures | |
| struct | observation |
| struct | cluster |
Macros | |
| #define | _USE_MATH_DEFINES /* required for MS Visual C */ |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct observation | observation |
| typedef struct cluster | cluster |
Functions | |
| int | calculateNearst (observation *o, cluster clusters[], int k) |
| void | calculateCentroid (observation observations[], size_t size, cluster *centroid) |
| cluster * | kMeans (observation observations[], size_t size, int k) |
| void | printEPS (observation pts[], size_t len, cluster cent[], int k) |
| static void | test () |
| void | test2 () |
| int | main () |
Detailed Description
K Means Clustering Algorithm implemented.
This file has K Means algorithm implemmented It prints test output in eps format
Note: Though the code for clustering works for all the 2D data points and can be extended for any size vector by making the required changes, but note that the output method i.e. printEPS is only good for polar data points i.e. in a circle and both test use the same.
Function Documentation
◆ main()
| int main | ( | void | ) |
◆ printEPS()
| void printEPS | ( | observation | pts[], |
| size_t | len, | ||
| cluster | cent[], | ||
| int | k | ||
| ) |
A function to print observations and clusters The code is taken from http://rosettacode.org/wiki/K-means%2B%2B_clustering. Even the K Means code is also inspired from it
- Note
- To print in a file use pipeline operator ./k_means_clustering > image.eps
- Parameters
-
observations observations array len size of observation array cent clusters centroid's array k size of cent array
◆ test()
|
static |
A function to test the kMeans function Generates 100000 points in a circle of radius 20.0 with center at (0,0) and cluster them into 5 clusters
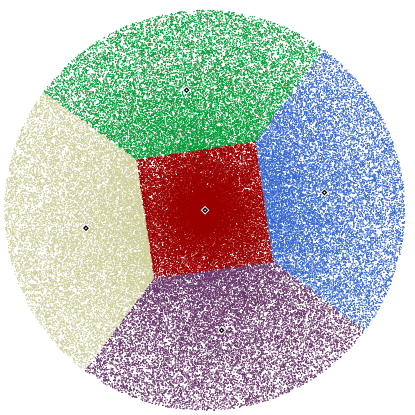
- Returns
- None
◆ test2()
| void test2 | ( | ) |
A function to test the kMeans function Generates 1000000 points in a circle of radius 20.0 with center at (0,0) and cluster them into 11 clusters
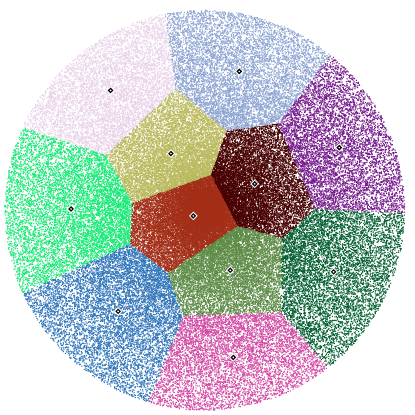
- Returns
- None