| .github/workflows | ||
| common | ||
| decompressor | ||
| host | ||
| man/man1 | ||
| stage1 | ||
| test | ||
| tinf | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| bochsrc | ||
| bootstrap | ||
| config.h.in | ||
| CONFIG.md | ||
| configure.ac | ||
| GNUmakefile.in | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| limine.h | ||
| PHILOSOPHY.md | ||
| PROTOCOL.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| screenshot.png | ||
| version.sh | ||
Limine
What is Limine?
Limine is a modern, advanced, portable, multiprotocol bootloader, also used as the reference implementation for the Limine boot protocol.
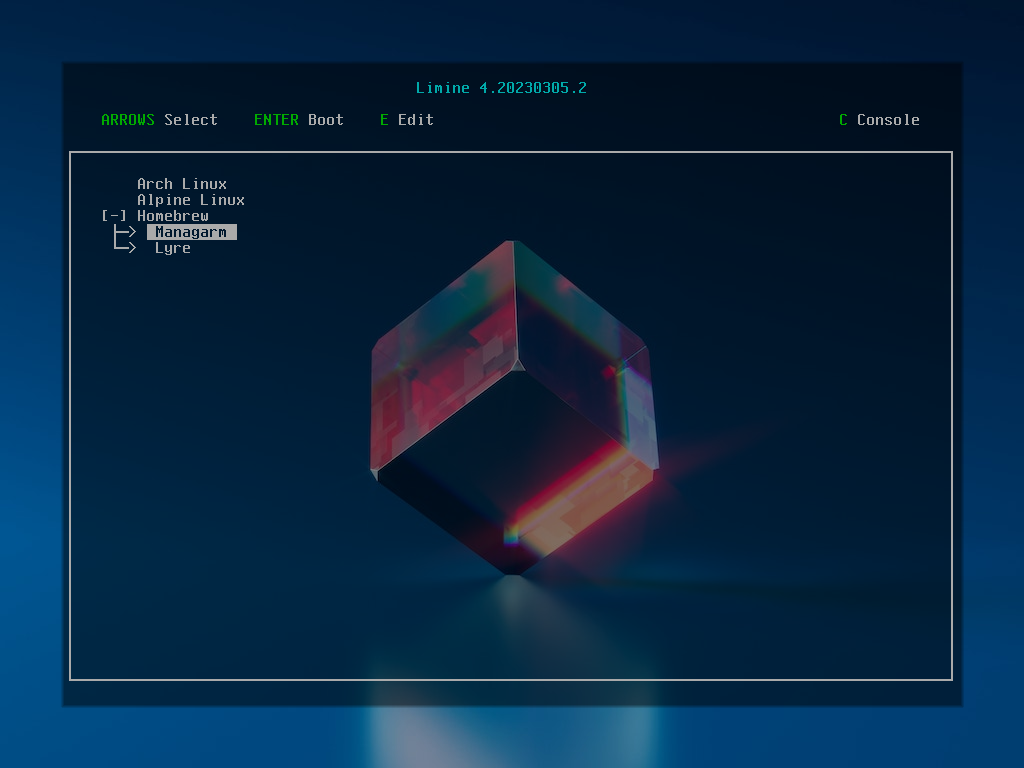
Limine's boot menu
Supported architectures
- IA-32 (32-bit x86)
- x86_64
- aarch64 (arm64)
Supported boot protocols
- Linux
- Limine
- Multiboot 1
- Multiboot 2
- Chainloading
Supported partitioning schemes
- MBR
- GPT
- Unpartitioned media
Supported filesystems
- ext2/3/4
- FAT12/16/32
- ISO9660 (CDs/DVDs)
If your filesystem isn't listed here, please read the philosophy first, especially before opening issues or pull requests related to this.
Minimum system requirements
For 32-bit x86 systems, support is only ensured starting with those with Pentium Pro (i686) class CPUs.
All x86_64 and aarch64 (UEFI) systems are supported.
Packaging status
Binary releases
For convenience, for point releases, binaries are distributed. These binaries
are shipped in the -binary branches and tags of this repository
(see branches and
tags).
For example, to clone the latest binary release of the v4.x branch one can do
git clone https://github.com/limine-bootloader/limine.git --branch=v4.x-branch-binary --depth=1
or, to clone a specific binary point release (for example v4.20230120.0)
git clone https://github.com/limine-bootloader/limine.git --branch=v4.20230120.0-binary --depth=1
In order to rebuild host utilities like limine-deploy, simply run make in the binary
release directory.
Host utility binaries are provided for Windows.
Building the bootloader
The following steps are not necessary if cloning a binary release. If so, skip to "Installing Limine binaries".
Prerequisites
In order to build Limine, the following programs have to be installed:
common UNIX tools (also known as coreutils),
GNU make, grep, sed, find, awk, gzip, nasm, mtools
(optional, necessary to build limine-cd-efi.bin).
Furthermore, gcc or llvm/clang must also be installed, alongside
the respective binutils.
Configure
If using a release tarball (recommended, see https://github.com/limine-bootloader/limine/releases),
run ./configure directly.
If checking out from the repository, run ./bootstrap first in order to download the
necessary dependencies and generate the configure script (GNU autoconf and GNU automake required).
./configure takes arguments and environment variables; for more information on
these, run ./configure --help.
./configure by default does not build any Limine port. Make sure to read the
output of ./configure --help and enable any or all ports!
Limine supports both in-tree and out-of-tree builds. Simply run the configure
script from the directory you wish to execute the build in. The following make
commands are supposed to be ran inside the build directory.
Building Limine
To build Limine, run:
make # (or gmake where applicable)
The generated bootloader files are going to be in ./bin.
Installing Limine binaries
This step is optional as the bootloader binaries can be used from the ./bin or
release directory just fine. This step will only install them to share, include, and
bin directories in the specified prefix (default is /usr/local, see
./configure --help, or the PREFIX variable if installing from a binary release).
To install Limine, run:
make install # (or gmake where applicable)
How to use
UEFI
The BOOT{IA32,X64,AA64}.EFI files are valid EFI applications that can be simply copied to
the /EFI/BOOT directory of a FAT formatted EFI system partition. These files can
be installed there and coexist with a BIOS installation of Limine (see below) so
that the disk will be bootable on both BIOS and UEFI systems.
The boot device must contain the limine.cfg files in
either the root, limine, boot, or boot/limine directory of one of the
partitions, formatted with a supported file system (the ESP partition is recommended).
Secure Boot
Limine can be booted with secure boot using shim. This will also allow one to enroll
the BLAKE2B hash of the Limine config file into the Limine EFI executable image itself for
verification purposes.
For more information see the limine-enroll-config program and the philosophy.
BIOS/MBR
In order to install Limine on a MBR device (which can just be a raw image file),
run limine-deploy as such:
limine-deploy <path to device/image>
The boot device must contain the limine.sys and limine.cfg files in
either the root, limine, boot, or boot/limine directory of one of the
partitions, formatted with a supported file system.
BIOS/GPT
If using a GPT formatted device, there are 2 options one can follow for installation:
- Specifying a dedicated stage 2 partition.
- Letting
limine-deployattempt to embed stage 2 within GPT structures.
In case one wants to specify a stage 2 partition, create a partition on the GPT
device of at least 32KiB in size, and pass the 1-based number of the partition
to limine-deploy as a second argument; such as:
limine-deploy <path to device/image> <1-based stage 2 partition number>
In case one wants to let limine-deploy embed stage 2 within GPT's structures,
simply omit the partition number, and invoke limine-deploy the same as one
would do for an MBR partitioned device.
The boot device must contain the limine.sys and limine.cfg files in
either the root, limine, boot, or boot/limine directory of one of the
partitions, formatted with a supported file system.
BIOS/UEFI hybrid ISO creation
In order to create a hybrid ISO with Limine, place the
limine-cd-efi.bin, limine-cd.bin, limine.sys, and limine.cfg files
into a directory which will serve as the root of the created ISO.
(limine.sys and limine.cfg must either be in the root, limine, boot, or
boot/limine directory; limine-cd-efi.bin and limine-cd.bin can reside
anywhere).
Place any other file you want to be on the final ISO in said directory, then run:
xorriso -as mkisofs -b <relative path of limine-cd.bin> \
-no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 -boot-info-table \
--efi-boot <relative path of limine-cd-efi.bin> \
-efi-boot-part --efi-boot-image --protective-msdos-label \
<root directory> -o image.iso
Note: xorriso is required.
And do not forget to also run limine-deploy on the generated image:
limine-deploy image.iso
<relative path of limine-cd.bin> is the relative path of
limine-cd.bin inside the root directory.
For example, if it was copied in <root directory>/boot/limine-cd.bin,
it would be boot/limine-cd.bin.
<relative path of limine-cd-efi.bin> is the relative path of
limine-cd-efi.bin inside the root directory.
For example, if it was copied in
<root directory>/boot/limine-cd-efi.bin, it would be
boot/limine-cd-efi.bin.
BIOS/PXE boot
The limine-pxe.bin binary is a valid PXE boot image.
In order to boot Limine from PXE it is necessary to setup a DHCP server with
support for PXE booting. This can either be accomplished using a single DHCP
server or your existing DHCP server and a proxy DHCP server such as dnsmasq.
limine.cfg and limine.sys are expected to be on the server used for boot.
UEFI/PXE boot
The BOOT{IA32,X64,AA64}.EFI files are compatible with UEFI PXE.
The steps needed to boot Limine are the same as with BIOS PXE,
except that you don't need limine.sys in the server.
Configuration
The limine.cfg file contains Limine's configuration.
An example limine.cfg file can be found in test/limine.cfg.
More info on the format of limine.cfg can be found in CONFIG.md.
Acknowledgments
Limine uses a stripped-down version of tinf for early GZIP decompression.
Limine relies on stb_image for runtime GZIP decompression and image loading.
Discord server
We have a Discord server if you need support, info, or you just want to hang out with us.