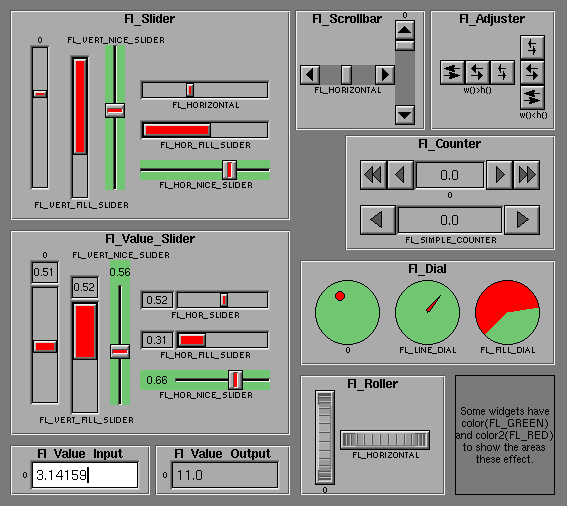
Fl_Widget
|
+----Fl_Valuator
|
+----Fl_Adjuster, Fl_Counter, Fl_Dial, Fl_Roller,
Fl_Slider, Fl_Value_Input, Fl_Value_Output,
#include <FL/Fl_Valuator.H>
There are probably more of these classes in fltk than any others:

In the above diagram each box surrounds an actual subclass. These
are further differentiated by setting the type() of the widget to the symbolic
value labeling the widget. The ones labelled "0" are the default
versions with a type(0). For consistency the symbol
FL_VERTICAL is defined as zero.
Methods
Fl_Valuator::Fl_Valuator(int x, int y, int w, int h, const char *label = 0)
Creates a new Fl_Valuator widget using the given position, size, and
label string. The default boxtype is FL_NO_BOX.
virtual Fl_Valuator::~Fl_Valuator()
Destroys the valuator.
double Fl_Valuator::value() const
Get or set the current value. The new value is not clamped or
otherwise changed before storing it. Use clamp() or
round() to modify the value before calling this if you want.
If the new value is different than the current one the object is
redrawn. The initial value is zero.
int Fl_Valuator::value(double)double Fl_Valuator::minimum() const
Gets or sets the minimum value for the valuator.
void Fl_Valuator::minimum(double)double Fl_Valuator::maximum() const
Gets or sets the maximum value for the valuator.
void Fl_Valuator::maximum(double)void Fl_Valuator::range(double min, double max);
Sets the minimum and maximum values for the valuator. When the user
manipulates the widget, the value is limited to this range. This
clamping is done after rounding to the step value (this makes a
difference if the range is not a multiple of the step).
The minimum may be greater than the maximum. This has the effect of "reversing" the object so the larger values are in the opposite direction. This also switches which end of the filled sliders is filled.
Some widgets consider this a "soft" range. This means they will stop at the range, but if the user releases and grabs the control again and tries to move it further, it is allowed.
The range may affect the display. You must redraw() the widget after changing the range.
For precision the step is stored as the ratio of two integers, A/B. You can set these integers directly. Currently setting a floating point value sets the nearest A/1 or 1/B value possible.