/**
* \file
* \brief [Adaptive Linear Neuron
* (ADALINE)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ADALINE) implementation
* \details
* 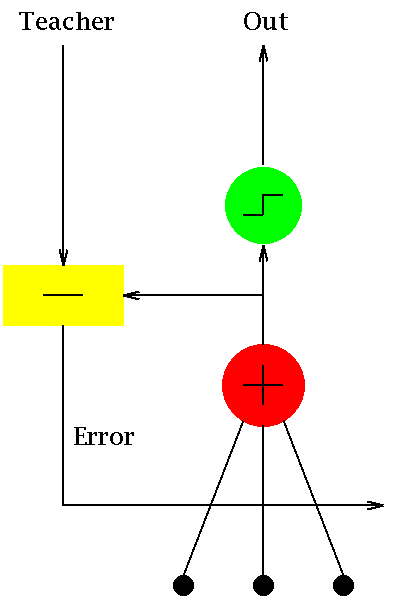 * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
* \sum_j x_jw_j+\theta
* \f]
* where \f$x_j\f$ are the input features of a sample, \f$w_j\f$ are the
* coefficients of the linear function and \f$\theta\f$ is a constant. If we
* know the \f$w_j\f$, then for any given set of features, \f$y\f$ can be
* computed. Computing the \f$w_j\f$ is a supervised learning algorithm wherein
* a set of features and their corresponding outputs are given and weights are
* computed using stochastic gradient descent method.
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/**
* @addtogroup machine_learning Machine learning algorithms
* @{
* @addtogroup adaline Adaline learning algorithm
* @{
*/
/** Maximum number of iterations to learn */
#define MAX_ADALINE_ITER 500 // INT_MAX
/** structure to hold adaline model parameters */
struct adaline
{
double eta; /**< learning rate of the algorithm */
double *weights; /**< weights of the neural network */
int num_weights; /**< number of weights of the neural network */
};
/** convergence accuracy \f$=1\times10^{-5}\f$ */
#define ADALINE_ACCURACY 1e-5
/**
* Default constructor
* \param[in] num_features number of features present
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.1)
* \returns new adaline model
*/
struct adaline new_adaline(const int num_features, const double eta)
{
if (eta <= 0.f || eta >= 1.f)
{
fprintf(stderr, "learning rate should be > 0 and < 1\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// additional weight is for the constant bias term
int num_weights = num_features + 1;
struct adaline ada;
ada.eta = eta;
ada.num_weights = num_weights;
ada.weights = (double *)malloc(num_weights * sizeof(double));
if (!ada.weights)
{
perror("Unable to allocate error for weights!");
return ada;
}
// initialize with random weights in the range [-50, 49]
for (int i = 0; i < num_weights; i++) ada.weights[i] = 1.f;
// ada.weights[i] = (double)(rand() % 100) - 50);
return ada;
}
/** delete dynamically allocated memory
* \param[in] ada model from which the memory is to be freed.
*/
void delete_adaline(struct adaline *ada)
{
if (ada == NULL)
return;
free(ada->weights);
};
/** [Heaviside activation
* function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heaviside_step_function)
* [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
* \sum_j x_jw_j+\theta
* \f]
* where \f$x_j\f$ are the input features of a sample, \f$w_j\f$ are the
* coefficients of the linear function and \f$\theta\f$ is a constant. If we
* know the \f$w_j\f$, then for any given set of features, \f$y\f$ can be
* computed. Computing the \f$w_j\f$ is a supervised learning algorithm wherein
* a set of features and their corresponding outputs are given and weights are
* computed using stochastic gradient descent method.
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/**
* @addtogroup machine_learning Machine learning algorithms
* @{
* @addtogroup adaline Adaline learning algorithm
* @{
*/
/** Maximum number of iterations to learn */
#define MAX_ADALINE_ITER 500 // INT_MAX
/** structure to hold adaline model parameters */
struct adaline
{
double eta; /**< learning rate of the algorithm */
double *weights; /**< weights of the neural network */
int num_weights; /**< number of weights of the neural network */
};
/** convergence accuracy \f$=1\times10^{-5}\f$ */
#define ADALINE_ACCURACY 1e-5
/**
* Default constructor
* \param[in] num_features number of features present
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.1)
* \returns new adaline model
*/
struct adaline new_adaline(const int num_features, const double eta)
{
if (eta <= 0.f || eta >= 1.f)
{
fprintf(stderr, "learning rate should be > 0 and < 1\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// additional weight is for the constant bias term
int num_weights = num_features + 1;
struct adaline ada;
ada.eta = eta;
ada.num_weights = num_weights;
ada.weights = (double *)malloc(num_weights * sizeof(double));
if (!ada.weights)
{
perror("Unable to allocate error for weights!");
return ada;
}
// initialize with random weights in the range [-50, 49]
for (int i = 0; i < num_weights; i++) ada.weights[i] = 1.f;
// ada.weights[i] = (double)(rand() % 100) - 50);
return ada;
}
/** delete dynamically allocated memory
* \param[in] ada model from which the memory is to be freed.
*/
void delete_adaline(struct adaline *ada)
{
if (ada == NULL)
return;
free(ada->weights);
};
/** [Heaviside activation
* function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heaviside_step_function)  * @param x activation function input
* @returns \f$f(x)= \begin{cases}1 & \forall\; x > 0\\ -1 & \forall\; x \le0
* \end{cases}\f$
*/
int adaline_activation(double x) { return x > 0 ? 1 : -1; }
/**
* Operator to print the weights of the model
* @param ada model for which the values to print
* @returns pointer to a NULL terminated string of formatted weights
*/
char *adaline_get_weights_str(const struct adaline *ada)
{
static char out[100]; // static so the value is persistent
sprintf(out, "<");
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights; i++)
{
sprintf(out, "%s%.4g", out, ada->weights[i]);
if (i < ada->num_weights - 1)
sprintf(out, "%s, ", out);
}
sprintf(out, "%s>", out);
return out;
}
/**
* predict the output of the model for given set of features
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to predict
* \param[in] x input vector
* \param[out] out optional argument to return neuron output before applying
* activation function (`NULL` to ignore)
* \returns model prediction output
*/
int adaline_predict(struct adaline *ada, const double *x, double *out)
{
double y = ada->weights[ada->num_weights - 1]; // assign bias value
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights - 1; i++) y += x[i] * ada->weights[i];
if (out) // if out variable is not NULL
*out = y;
// quantizer: apply ADALINE threshold function
return adaline_activation(y);
}
/**
* Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for one feature
* vector
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to fit
* \param[in] x feature vector
* \param[in] y known output value
* \returns correction factor
*/
double adaline_fit_sample(struct adaline *ada, const double *x, const int y)
{
/* output of the model with current weights */
int p = adaline_predict(ada, x, NULL);
int prediction_error = y - p; // error in estimation
double correction_factor = ada->eta * prediction_error;
/* update each weight, the last weight is the bias term */
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights - 1; i++)
{
ada->weights[i] += correction_factor * x[i];
}
ada->weights[ada->num_weights - 1] += correction_factor; // update bias
return correction_factor;
}
/**
* Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for an array of
* vectors.
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to train
* \param[in] X array of feature vector
* \param[in] y known output value for each feature vector
* \param[in] N number of training samples
*/
void adaline_fit(struct adaline *ada, double **X, const int *y, const int N)
{
double avg_pred_error = 1.f;
int iter;
for (iter = 0;
(iter < MAX_ADALINE_ITER) && (avg_pred_error > ADALINE_ACCURACY);
iter++)
{
avg_pred_error = 0.f;
// perform fit for each sample
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double err = adaline_fit_sample(ada, X[i], y[i]);
avg_pred_error += fabs(err);
}
avg_pred_error /= N;
// Print updates every 200th iteration
// if (iter % 100 == 0)
printf("\tIter %3d: Training weights: %s\tAvg error: %.4f\n", iter,
adaline_get_weights_str(ada), avg_pred_error);
}
if (iter < MAX_ADALINE_ITER)
printf("Converged after %d iterations.\n", iter);
else
printf("Did not converged after %d iterations.\n", iter);
}
/** @}
* @}
*/
/**
* test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line
* \f$x=y\f$ as +1 and others as -1.
* Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features.
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test1(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(2, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 10; // number of sample points
const double saved_X[10][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, -2}, {2, 3}, {3, -1},
{4, 1}, {6, -5}, {-7, -3}, {-8, 5},
{-9, 2}, {-10, -15}};
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
const int Y[10] = {1, -1, 1, -1, -1,
-1, 1, 1, 1, -1}; // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
X[i] = (double *)saved_X[i];
}
printf("------- Test 1 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
double test_x[] = {5, -3};
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(5,-3): % d\n", pred);
assert(pred == -1);
printf(" ...passed\n");
double test_x2[] = {5, 8};
pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x2, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(5, 8): % d\n", pred);
assert(pred == 1);
printf(" ...passed\n");
// for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
// free(X[i]);
free(X);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/**
* test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line
* \f$x+3y=-1\f$ as +1 and others as -1.
* Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features.
* The function will create random sample points for training and test purposes.
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test2(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(2, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 50; // number of sample points
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
int *Y = (int *)malloc(N * sizeof(int)); // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) X[i] = (double *)malloc(2 * sizeof(double));
// generate sample points in the interval
// [-range2/100 , (range2-1)/100]
int range = 500; // sample points full-range
int range2 = range >> 1; // sample points half-range
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
X[i][0] = x0;
X[i][1] = x1;
Y[i] = (x0 + 3. * x1) > -1 ? 1 : -1;
}
printf("------- Test 2 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
int N_test_cases = 5;
double test_x[2];
for (int i = 0; i < N_test_cases; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
test_x[0] = x0;
test_x[1] = x1;
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(% 3.2f,% 3.2f): % d\n", x0, x1, pred);
int expected_val = (x0 + 3. * x1) > -1 ? 1 : -1;
assert(pred == expected_val);
printf(" ...passed\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) free(X[i]);
free(X);
free(Y);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/**
* test function to predict points in a 3D coordinate system lying within the
* sphere of radius 1 and centre at origin as +1 and others as -1. Note that
* each point is defined by 3 values but we use 6 features. The function will
* create random sample points for training and test purposes.
* The sphere centred at origin and radius 1 is defined as:
* \f$x^2+y^2+z^2=r^2=1\f$ and if the \f$r^2<1\f$, point lies within the sphere
* else, outside.
*
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test3(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(6, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 50; // number of sample points
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
int *Y = (int *)malloc(N * sizeof(int)); // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) X[i] = (double *)malloc(6 * sizeof(double));
// generate sample points in the interval
// [-range2/100 , (range2-1)/100]
int range = 200; // sample points full-range
int range2 = range >> 1; // sample points half-range
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x2 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
X[i][0] = x0;
X[i][1] = x1;
X[i][2] = x2;
X[i][3] = x0 * x0;
X[i][4] = x1 * x1;
X[i][5] = x2 * x2;
Y[i] = (x0 * x0 + x1 * x1 + x2 * x2) <= 1 ? 1 : -1;
}
printf("------- Test 3 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
int N_test_cases = 5;
double test_x[6];
for (int i = 0; i < N_test_cases; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x2 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
test_x[0] = x0;
test_x[1] = x1;
test_x[2] = x2;
test_x[3] = x0 * x0;
test_x[4] = x1 * x1;
test_x[5] = x2 * x2;
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(% 3.2f,% 3.2f): % d\n", x0, x1, pred);
int expected_val = (x0 * x0 + x1 * x1 + x2 * x2) <= 1 ? 1 : -1;
assert(pred == expected_val);
printf(" ...passed\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) free(X[i]);
free(X);
free(Y);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/** Main function */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
srand(time(NULL)); // initialize random number generator
double eta = 0.1; // default value of eta
if (argc == 2) // read eta value from commandline argument if present
eta = strtof(argv[1], NULL);
test1(eta);
printf("Press ENTER to continue...\n");
getchar();
test2(eta);
printf("Press ENTER to continue...\n");
getchar();
test3(eta);
return 0;
}
* @param x activation function input
* @returns \f$f(x)= \begin{cases}1 & \forall\; x > 0\\ -1 & \forall\; x \le0
* \end{cases}\f$
*/
int adaline_activation(double x) { return x > 0 ? 1 : -1; }
/**
* Operator to print the weights of the model
* @param ada model for which the values to print
* @returns pointer to a NULL terminated string of formatted weights
*/
char *adaline_get_weights_str(const struct adaline *ada)
{
static char out[100]; // static so the value is persistent
sprintf(out, "<");
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights; i++)
{
sprintf(out, "%s%.4g", out, ada->weights[i]);
if (i < ada->num_weights - 1)
sprintf(out, "%s, ", out);
}
sprintf(out, "%s>", out);
return out;
}
/**
* predict the output of the model for given set of features
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to predict
* \param[in] x input vector
* \param[out] out optional argument to return neuron output before applying
* activation function (`NULL` to ignore)
* \returns model prediction output
*/
int adaline_predict(struct adaline *ada, const double *x, double *out)
{
double y = ada->weights[ada->num_weights - 1]; // assign bias value
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights - 1; i++) y += x[i] * ada->weights[i];
if (out) // if out variable is not NULL
*out = y;
// quantizer: apply ADALINE threshold function
return adaline_activation(y);
}
/**
* Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for one feature
* vector
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to fit
* \param[in] x feature vector
* \param[in] y known output value
* \returns correction factor
*/
double adaline_fit_sample(struct adaline *ada, const double *x, const int y)
{
/* output of the model with current weights */
int p = adaline_predict(ada, x, NULL);
int prediction_error = y - p; // error in estimation
double correction_factor = ada->eta * prediction_error;
/* update each weight, the last weight is the bias term */
for (int i = 0; i < ada->num_weights - 1; i++)
{
ada->weights[i] += correction_factor * x[i];
}
ada->weights[ada->num_weights - 1] += correction_factor; // update bias
return correction_factor;
}
/**
* Update the weights of the model using supervised learning for an array of
* vectors.
*
* \param[in] ada adaline model to train
* \param[in] X array of feature vector
* \param[in] y known output value for each feature vector
* \param[in] N number of training samples
*/
void adaline_fit(struct adaline *ada, double **X, const int *y, const int N)
{
double avg_pred_error = 1.f;
int iter;
for (iter = 0;
(iter < MAX_ADALINE_ITER) && (avg_pred_error > ADALINE_ACCURACY);
iter++)
{
avg_pred_error = 0.f;
// perform fit for each sample
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double err = adaline_fit_sample(ada, X[i], y[i]);
avg_pred_error += fabs(err);
}
avg_pred_error /= N;
// Print updates every 200th iteration
// if (iter % 100 == 0)
printf("\tIter %3d: Training weights: %s\tAvg error: %.4f\n", iter,
adaline_get_weights_str(ada), avg_pred_error);
}
if (iter < MAX_ADALINE_ITER)
printf("Converged after %d iterations.\n", iter);
else
printf("Did not converged after %d iterations.\n", iter);
}
/** @}
* @}
*/
/**
* test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line
* \f$x=y\f$ as +1 and others as -1.
* Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features.
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test1(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(2, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 10; // number of sample points
const double saved_X[10][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, -2}, {2, 3}, {3, -1},
{4, 1}, {6, -5}, {-7, -3}, {-8, 5},
{-9, 2}, {-10, -15}};
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
const int Y[10] = {1, -1, 1, -1, -1,
-1, 1, 1, 1, -1}; // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
X[i] = (double *)saved_X[i];
}
printf("------- Test 1 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
double test_x[] = {5, -3};
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(5,-3): % d\n", pred);
assert(pred == -1);
printf(" ...passed\n");
double test_x2[] = {5, 8};
pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x2, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(5, 8): % d\n", pred);
assert(pred == 1);
printf(" ...passed\n");
// for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
// free(X[i]);
free(X);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/**
* test function to predict points in a 2D coordinate system above the line
* \f$x+3y=-1\f$ as +1 and others as -1.
* Note that each point is defined by 2 values or 2 features.
* The function will create random sample points for training and test purposes.
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test2(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(2, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 50; // number of sample points
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
int *Y = (int *)malloc(N * sizeof(int)); // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) X[i] = (double *)malloc(2 * sizeof(double));
// generate sample points in the interval
// [-range2/100 , (range2-1)/100]
int range = 500; // sample points full-range
int range2 = range >> 1; // sample points half-range
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
X[i][0] = x0;
X[i][1] = x1;
Y[i] = (x0 + 3. * x1) > -1 ? 1 : -1;
}
printf("------- Test 2 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
int N_test_cases = 5;
double test_x[2];
for (int i = 0; i < N_test_cases; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
test_x[0] = x0;
test_x[1] = x1;
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(% 3.2f,% 3.2f): % d\n", x0, x1, pred);
int expected_val = (x0 + 3. * x1) > -1 ? 1 : -1;
assert(pred == expected_val);
printf(" ...passed\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) free(X[i]);
free(X);
free(Y);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/**
* test function to predict points in a 3D coordinate system lying within the
* sphere of radius 1 and centre at origin as +1 and others as -1. Note that
* each point is defined by 3 values but we use 6 features. The function will
* create random sample points for training and test purposes.
* The sphere centred at origin and radius 1 is defined as:
* \f$x^2+y^2+z^2=r^2=1\f$ and if the \f$r^2<1\f$, point lies within the sphere
* else, outside.
*
* \param[in] eta learning rate (optional, default=0.01)
*/
void test3(double eta)
{
struct adaline ada = new_adaline(6, eta); // 2 features
const int N = 50; // number of sample points
double **X = (double **)malloc(N * sizeof(double *));
int *Y = (int *)malloc(N * sizeof(int)); // corresponding y-values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) X[i] = (double *)malloc(6 * sizeof(double));
// generate sample points in the interval
// [-range2/100 , (range2-1)/100]
int range = 200; // sample points full-range
int range2 = range >> 1; // sample points half-range
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x2 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
X[i][0] = x0;
X[i][1] = x1;
X[i][2] = x2;
X[i][3] = x0 * x0;
X[i][4] = x1 * x1;
X[i][5] = x2 * x2;
Y[i] = (x0 * x0 + x1 * x1 + x2 * x2) <= 1 ? 1 : -1;
}
printf("------- Test 3 -------\n");
printf("Model before fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
adaline_fit(&ada, X, Y, N);
printf("Model after fit: %s\n", adaline_get_weights_str(&ada));
int N_test_cases = 5;
double test_x[6];
for (int i = 0; i < N_test_cases; i++)
{
double x0 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x1 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
double x2 = ((rand() % range) - range2) / 100.f;
test_x[0] = x0;
test_x[1] = x1;
test_x[2] = x2;
test_x[3] = x0 * x0;
test_x[4] = x1 * x1;
test_x[5] = x2 * x2;
int pred = adaline_predict(&ada, test_x, NULL);
printf("Predict for x=(% 3.2f,% 3.2f): % d\n", x0, x1, pred);
int expected_val = (x0 * x0 + x1 * x1 + x2 * x2) <= 1 ? 1 : -1;
assert(pred == expected_val);
printf(" ...passed\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) free(X[i]);
free(X);
free(Y);
delete_adaline(&ada);
}
/** Main function */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
srand(time(NULL)); // initialize random number generator
double eta = 0.1; // default value of eta
if (argc == 2) // read eta value from commandline argument if present
eta = strtof(argv[1], NULL);
test1(eta);
printf("Press ENTER to continue...\n");
getchar();
test2(eta);
printf("Press ENTER to continue...\n");
getchar();
test3(eta);
return 0;
}
 * [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
* \sum_j x_jw_j+\theta
* \f]
* where \f$x_j\f$ are the input features of a sample, \f$w_j\f$ are the
* coefficients of the linear function and \f$\theta\f$ is a constant. If we
* know the \f$w_j\f$, then for any given set of features, \f$y\f$ can be
* computed. Computing the \f$w_j\f$ is a supervised learning algorithm wherein
* a set of features and their corresponding outputs are given and weights are
* computed using stochastic gradient descent method.
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include
* [source](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Adaline_flow_chart.gif)
* ADALINE is one of the first and simplest single layer artificial neural
* network. The algorithm essentially implements a linear function
* \f[ f\left(x_0,x_1,x_2,\ldots\right) =
* \sum_j x_jw_j+\theta
* \f]
* where \f$x_j\f$ are the input features of a sample, \f$w_j\f$ are the
* coefficients of the linear function and \f$\theta\f$ is a constant. If we
* know the \f$w_j\f$, then for any given set of features, \f$y\f$ can be
* computed. Computing the \f$w_j\f$ is a supervised learning algorithm wherein
* a set of features and their corresponding outputs are given and weights are
* computed using stochastic gradient descent method.
* \author [Krishna Vedala](https://github.com/kvedala)
*/
#include