| demo | ||
| screen | ||
| gui.c | ||
| gui.h | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Readme.md | ||
| stb_rect_pack.h | ||
| stb_truetype.h | ||
Zahnrad
This is a bloat free minimal state immediate mode graphical user interface toolkit written in ANSI C. It was designed as a simple embeddable user interface for application and does not have any direct dependencies.
Features
- Immediate mode graphical user interface toolkit
- Written in C89 (ANSI C)
- Small codebase (~8kLOC)
- Focus on portability, efficiency, simplicity and minimal internal state
- No global or hidden state
- No direct dependencies
- Configurable style and colors
- UTF-8 support
- Optional vertex buffer output and font handling
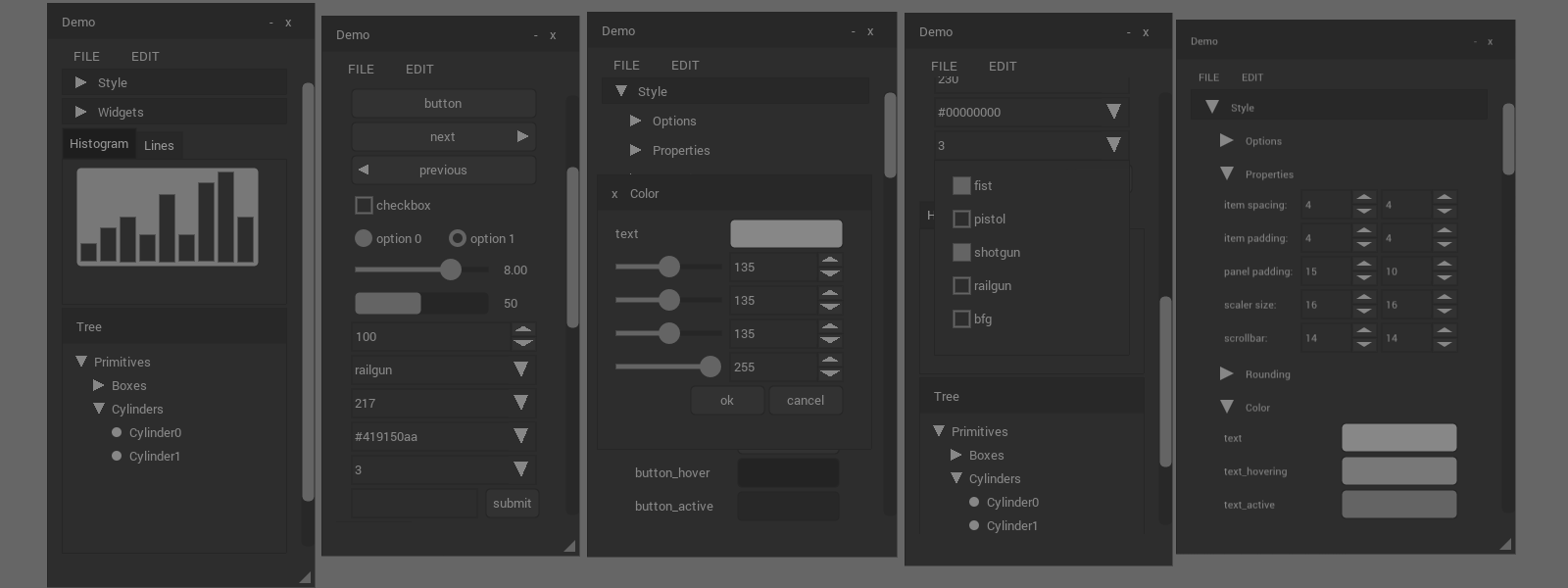
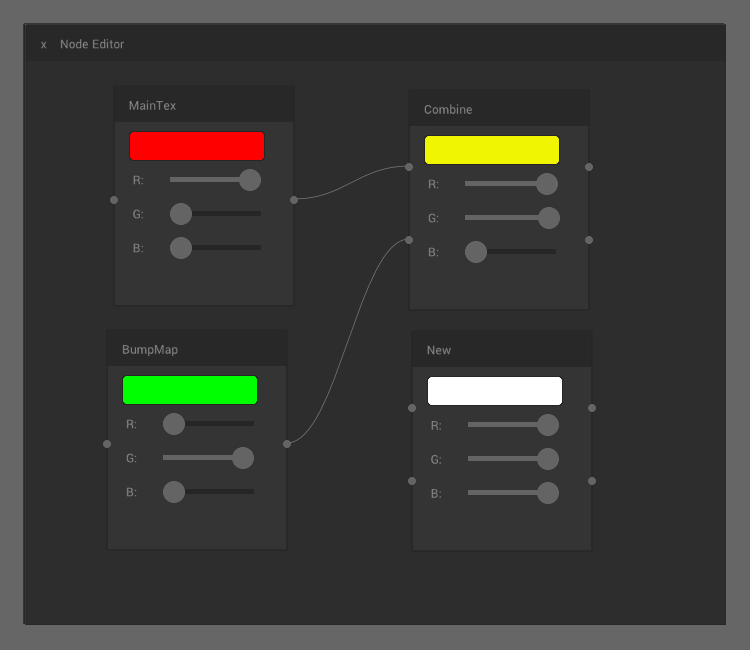
Gallery
Example
/* setup configuration */
struct gui_style style;
struct gui_user_font font = {...};
gui_style_default(&style, GUI_DEFAULT_ALL, &font);
/* allocate memory to hold draw commands */
struct gui_command_queue queue;
gui_command_queue_init_fixed(&queue, malloc(MEMORY_SIZE), MEMORY_SIZE);
/* initialize panel */
struct gui_window panel;
gui_window_init(&panel, 50, 50, 220, 180,
GUI_PANEL_BORDER|GUI_PANEL_MOVEABLE|GUI_PANEL_SCALEABLE,
&queue, &style, &input);
/* setup widget data */
enum {EASY, HARD};
gui_size option = EASY;
gui_size item = 0;
gui_state active = 0;
struct gui_input input = {0};
while (1) {
gui_input_begin(&input);
/* record input */
gui_input_end(&input);
/* GUI */
struct gui_context context;
gui_begin(&context, &panel);
{
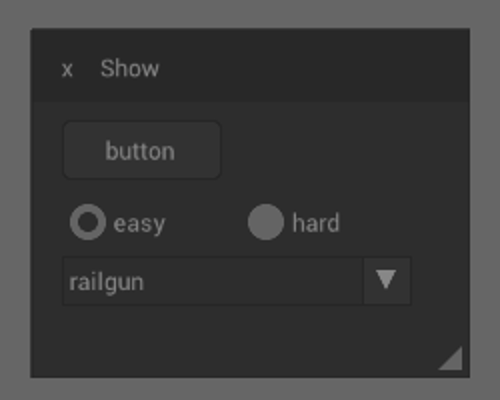
const char *items[] = {"Fist", "Pistol", "Railgun", "BFG"};
gui_header(&context, "Show", GUI_CLOSEABLE, 0, GUI_HEADER_LEFT);
gui_layout_row_static(&context, 30, 80, 1);
if (gui_button_text(&context, "button", GUI_BUTTON_DEFAULT)) {
/* event handling */
}
gui_layout_row_dynamic(&context, 30, 2);
if (gui_option(&context, "easy", option == EASY)) option = EASY;
if (gui_option(&context, "hard", option == HARD)) option = HARD;
gui_label(&context, "Weapon:", GUI_TEXT_LEFT);
gui_combo(&context, items, LEN(items), &item, 20, &active);
}
gui_end(&context, &panel);
/* draw */
const struct gui_command *cmd;
gui_foreach_command(cmd, &queue) {
/* execute draw call command */
}
gui_command_queue_clear(&queue);
}
IMGUIs
Immediate mode in contrast to classical retained mode GUIs store as little state as possible by using procedural function calls as "widgets" instead of storing objects. Each "widget" function call takes hereby all its necessary data and immediately returns the user modified state back to the caller. Immediate mode graphical user interfaces therefore combine drawing and input handling into one unit instead of separating them like retain mode GUIs.
Since there is no to minimal internal state in immediate mode user interfaces, updates have to occur every frame, on every user input update or program state change which on one hand is more drawing expensive than classic retained GUI implementations but on the other hand grants a lot more flexibility and support for overall layout changes. In addition without any state there is no duplicated state between your program, the gui and the user which greatly simplifies code. Further traits of immediate mode graphic user interfaces are a code driven style, centralized flow control, easy extensibility and understandability.
FAQ
Where is the demo/example code?
The demo and example code can be found in the demo folder. There is demo code for Linux(X11) and nanovg.
Why did you use ANSI C and not C99 or C++?
Personally I stay out of all "discussions" about C vs C++ since they are totally worthless and never brought anything good with it. The simple answer is I personally love C and have nothing against people using C++ especially the new iterations with C++11 and C++14. While this hopefully settles my view on C vs C++ there is still ANSI C vs C99. While for personal projects I only use C99 with all its niceties, libraries are a little bit different. Libraries are designed to reach the highest number of users possible which brings me to ANSI C as the most portable version. In addition not all C compiler like the MSVC compiler fully support C99, which finalized my decision to use ANSI C.
Why do you typedef your own types instead of using the standard types?
This Project uses ANSI C which does not have the header file <stdint.h>
and therefore does not provide the fixed sized types that I need. Therefore
I defined my own types which need to be set to the correct size for each
platform. But if your development environment provides the header file you can define
GUI_USE_FIXED_SIZE_TYPES to directly use the correct types.
References
- Tutorial from Jari Komppa about imgui libraries
- Johannes 'johno' Norneby's article
- ImGui: The inspiration for this project from ocornut
- Nvidia's imgui toolkit
License
(The MIT License)