| Index |
|
Rezolvarea problemelor cu hardware admis Conectarea la o rețea wireless Conectarea din linie de comandă Sfaturi |
Seminar: Rețelistică Wireless
Getting the networking to run is essential in today's need for permanent internet connection. As keeping up to date with all the different and ever changing hardware and drivers is quite impossible for a small project, Haiku relies on a FreeBSD compatibility layer for its networking drivers.
This ensures a massive amount of supported hardware, though probably not 100% of what's out there. See this list online for a list of supported models or check FreeBSD 11.1's release hardware notes.
PCMCIA, CardBus, ExpressCard, USB and ISA devices still need more work to become functional.
 Rezolvarea problemelor cu hardware compatibil
Rezolvarea problemelor cu hardware compatibil
Even if the first hurdle of generally supported hardware is taken, some wireless network cards require binary firmware modules to properly operate. Haiku cannot include some of these proprietary firmware files due to licensing issues. Haiku does however include a simple script which will retrieve and install all of the needed proprietary bits for you. Generally, if you are planning to use wireless networking, it is a good idea to run this script to ensure your system has all of these firmwares available when they are needed.
Deschideți un Terminal și scrieți:
install-wifi-firmwares.sh
Revizuiți licențele și acceptați-le pentru a instala toate fișierele firmware disponibile acum.
Dacă nu aveți acces la Internet pentru a descărca firmware lipsă în Haiku, există o metodă deconectată, vedeți sfaturile de mai jos.
 Conectarea la o rețea wireless
Conectarea la o rețea wireless
By default, Haiku will join the first unencrypted wireless network it finds after booting up. To connect to a specific network, you use the Desktop applet NetworkStatus.
Right-click on its icon in the Deskbar and choose the network's public name (which is the "SSID" it broadcasts) from the context menu.

A window opens where you enter the type of authentication (probably WPA/WPA2, WEP is not a secure encryption anymore!) and the password for that wireless network. Click to start the login process.
Depending on your hardware and network configuration this may take a while. You'll be kept informed of the progress by notifications:
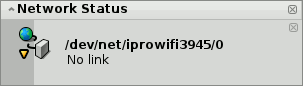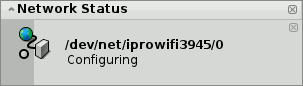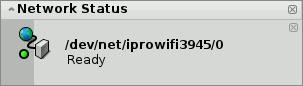
Once it reads "Ready" and the NetworkStatus icon in the Deskbar shows a green round light, the connection is established. If the notifications end in "No link" and a yellow triangle, something went wrong, probably an incorrect password.
 Conectarea din linie de comandă
Conectarea din linie de comandă
Dacă preferați să utilizați linia de comandă sau doriți să folosiți scriptare sau ~/config/settings/boot/UserBootscript pentru a automatiza pașii de alăturare unei rețele specifice la pornire, există comanda ifconfig.
Deschideți un Terminal și introduceți prima linie care scanează pentru rețele wireless disponibile:
ifconfig /dev/net/iprowifi3945/0 scan name address signal auth haiku-top 01:d0:19:a6:88:42 30 WPA ArcorInternet123 00:20:12:a4:29:e1 15 WPA
Desigur, calea către adaptorul de rețea wireless trebuie să fie ajustată.
Rezultatul arată numele public (SSID), adresa MAC, puterea semnalului și metoda de autentificare pentru toate rețelele găsite.
Pentru a vă alătura unei rețele, utilizați această linie și introduceți respectivul nume public (SSID) și parolă:
ifconfig /dev/net/iprowifi3945/0 join {SSID} {password}
Make sure the initial configuration of the wireless network adapter after booting up has finished, before issuing ifconfig commands or they might be ignored. Depending on your hardware and network configuration that may take a while. Watch those notifications...
 Sfaturi
Sfaturi
Descărcare deconectată de fișiere binare firmware
If you cannot obtain the binary firmware files via the install-wifi-firmwares.sh script (for example due to lack of internet connection within Haiku), you can also download this shell script, and run it from another OS that has wget and zip installed.
Windows users need to have wget and zip for Windows installed in their default locations and use this batch script.
The script will download the needed files and create a zip file that is to be extracted to Haiku's /boot. Once unpacked, open a Terminal and type:
install-wifi-firmwares.sh
Revizuiți licențele și acceptați-le pentru a instala toate fișierele firmware disponibile acum.
Evitarea pierderii conexiunii
Haiku's drivers for some WLAN chipsets like the iprowifi4965 are prone to lose connection when using WPA encryption. If you're affected by that, try to disable the "HT mode" (high throughput, 802.11n) before connecting to a network:
ifconfig /dev/net/iprowifi4965/0 -ht
Dacă asta rezolvă problema, adăugați linia la ~/config/settings/boot/UserBootscript pentru a o aplica automat la fiecare pornire.
 Română
Română Català
Català Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Español
Español Français
Français Italiano
Italiano Magyar
Magyar Polski
Polski Português
Português Português (Brazil)
Português (Brazil) Slovenčina
Slovenčina Suomi
Suomi Svenska
Svenska 中文 [中文]
中文 [中文] Русский
Русский Українська
Українська 日本語
日本語