Disposición del sistema de archivos
El sistema de archivos de Haiku es muy transparente, siempre intenta usar nombres lógicos para sus archivos y carpetas que no confundan el usuario. Los archivos y carpetas que son de importancia para el sistema para funcionar apropiadamente se protegen de la modificación accidental, mostrando uno de estos avisos:
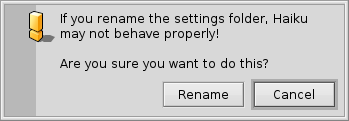
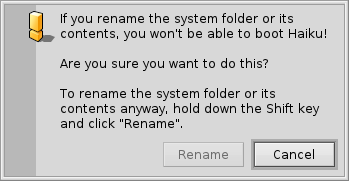
The second alert pops up if you try to rename or delete something in the system hierarchy. Here, the "" button will only become clickable when you're holding down the SHIFT key.
Generally, there are two separate branches springing from the root folder of the boot volume:
| /boot/system/ | Contains system files and applications/packages shared by all users. | |
| /boot/home/ | This is your personal folder where you keep your data and settings and the applications/packages that are not shared by all users. |
As long as Haiku isn't multi-user, this distinction between shared and not-shared applications/packages has no apparent effect, as there's only one user with one home folder. But since there will be support for more users than one eventually, it makes sense to learn the right way from the start.
 La carpeta del sistema - /boot/system/
La carpeta del sistema - /boot/system/
Under Haiku's predecessor BeOS, this folder was named /boot/beos/. You may still find it in some older documentation (e.g. in the original BeBook).
Most of the folders inside /boot/system/ are read-only, which is sensible as they contain the files necessary for Haiku to function correctly and therefore have to be safe from (accidental) alteration. The only user-writable folders are:
| /boot/system/cache/ | Contains cached files and the temporary folder linked to /tmp/. | |
| /boot/system/non-packaged/ | Contains a hierarchy for files that aren't part of a .hpkg (probably from old BeOS archives). | |
| /boot/system/packages/ | Besides holding Haiku's system packages, you can add/remove packages shared by all users. | |
| /boot/system/settings/ | Contains system-wide settings. | |
| /boot/system/var/ | Contains logs like the syslog (important when troubleshooting) and is the default location for the swap file. |
For more information on the packages and non-packaged folders, see topic Installing applications.
 La carpeta de inicio - /boot/home/
La carpeta de inicio - /boot/home/
This folder belongs to you. Here you can create and delete files and folders as you wish. (By the way, the tilde ("~") is a shortcut for your home folder, so you don't always have to write "/boot/home/" in Terminal.)
Files that you'd like to share with other users in a future multi-user environment have do be put outside /boot/home/. For example, you could create a folder /boot/all-users/ and put the stuff there.
| ~/Desktop/ | Holds the files of your desktop. Double-clicking won't open it, as it is already always visible. When your files happen to be obscured by open windows, just switch quickly to another Workspace. Of course, drilling down by right-clicking is also possible. | |
| ~/mail/ | This is the default location for your mails. | |
| ~/people/ | This is the default location for you contact files, see People. | |
| ~/queries/ | Queries are stored here, by default temporarily for 7 days. |
The folder /boot/home/config/ is special: just like /boot/system/ it's mostly under the control of the package management and therefore read-only. It too contains these similar user-writable folders:
| ~/config/packages/ | Here you can add/remove packages that are not shared by all users. | |
| ~/config/non-packaged/ | Contains a hierarchy for files that aren't part of a .hpkg (probably from old BeOS archives) and are not shared by all users. | |
| ~/config/settings/ | Esta carpeta contiene las selecciones para todas las aplicaciones y unas cuantas configuraciones para el sistema. Algunas aplicaciones administran sus configuraciones en sus propias subcarpetas, otros simplemente ponen su archivo de configuración allí. |
For more information on the packages and non-packaged folders, see topic Installing applications.
Here are some of the more interesting subfolders in ~/config/settings/:
| boot/ | Esta carpeta es el lugar para Scripts de usuario que se ejecutan antes que el sistema inicie o se apague. | |
| boot/launch/ | Enlaza a programas o documentos en esta carpeta que automáticamente se ejecutan en cada inicio. | |
| beos_mime/ | En esta base de datos MIME Haiku mantiene récord de todos los distintos tipos de archivo y sus selecciones. | |
| deskbar/menu/ | Copied or linked to files/folders/queries in this folder appear in the Deskbar menu. | |
| kernel/drivers/ | Hay un archivo de configuraciones que puede ser de interés: kernel ofrece configuraciones de bajo nivel como deshabilitar SMP, activar depuración serial o habilitar administración de energía avanzada. Se activa la línea de configuración removiendo el símbolo de comentario "#". ¡Sea cuidadoso aquí! | |
| Tracker/ | Además de los varios archivos de configuración para Tracker, hay algunas subcarpetas interesantes: | |
| DefaultFolderTemplate/ | Muestra y arregla todos los atributos y el tamaño de la ventana a su gusto. Cada carpeta nueva que se cree la usará como plantilla. | |
| DefaultQueryTemplates/ | Se puede definir la disposición de las ventanas de resultado de consulta para ciertos tipos de archivo. Vea el tema Consultas: la ventana de resultados. | |
| Go/ | Coloca enlaces a sus ubicaciones favoritas aquí para tenerlas disponibles, p. ej., en los paneles abrir y guardar. Vea el tema GUI de Haiku: Favoritos y carpetas recientes. | |
| Tracker New Template/ | Agregue una plantilla para cualquier tipo de archivo que luego estará disponible en el menú (Archivo | Nuevo) de Tracker. Vea el tema Tracker: Trabajar con archivos. |
 Español
Español Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Русский
Русский Svenska
Svenska 日本語
日本語 Українська
Українська 中文 [中文]
中文 [中文] Português
Português Suomi
Suomi Slovenčina
Slovenčina Magyar
Magyar Português (Brazil)
Português (Brazil) Català
Català Polski
Polski English
English